Discover essential traditional skills that empower independence, problem solving, and practical knowledge for youth today.

Traditional skills encompass hands-on abilities like gardening, woodworking, sewing, and basic first aid that have been passed down through generations. These skills focus on practical tasks such as food preservation, navigation, fire building, and handicrafts that teach self-sufficiency and resourcefulness.
Understanding and teaching these skills matters because they help younger generations develop confidence, creativity, and resilience in real-life situations. Integrating hands-on practice into everyday learning encourages curiosity and equips youth with valuable tools that remain relevant beyond the digital age.
1. Teach basic cooking techniques to build confidence in the kitchen.

Basic cooking techniques are foundational skills that teach how heat transforms ingredients, how to use knives safely and how to balance flavors and textures. Hands-on practice with simple methods like sautéing, roasting, boiling and seasoning builds intuition about timing, measurements and substitutions while demystifying recipes and equipment.
These skills promote independence, healthier eating and better budgeting while boosting confidence. Practical idea is to practice one new technique weekly, start with reliable recipes, and teach knife safety and hot surface awareness. Avoid assuming complexity and encourage tasting and adjusting. Safety note supervise young cooks and consult qualified food safety resources for questions about raw proteins or allergies.
2. Pass down sewing and mending skills for sustainable clothing care.

Sewing and mending teach how to repair garments, adjust fit and create simple items using basic stitches, seams and tools. Learning hand stitches like running stitch and backstitch as well as basic machine operation gives practical understanding of materials, seam allowances and thread choices through small projects.
This skill reduces waste, stretches clothing budgets and fosters creativity. Build a small repair kit with needles, neutral thread, snips, pins and a thimble, and practice invisible hems first. Rule of thumb mend early before small damage grows. Safety note handle needles carefully and supervise children until they can work safely.
3. Share gardening knowledge to encourage self-sufficiency and patience.
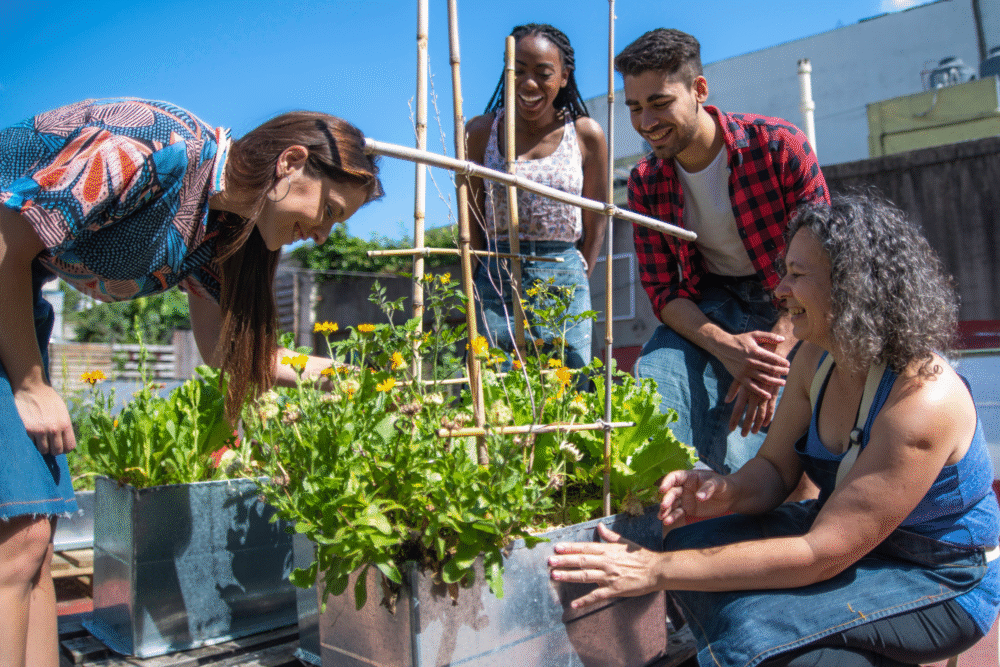
Gardening covers soil basics, plant selection, planting techniques, watering and watching for pests and disease. Hands-on tasks like starting seeds, transplanting and mulching teach how roots, light and nutrients interact and build practical know-how about plant care.
Gardening matters because it teaches patience, provides fresh produce or beauty, and encourages planning and resilience. Begin with containers or a small bed, improve soil with compost and learn to identify common pests early. Rule of thumb water when the top inch of soil feels dry and mulch to retain moisture. Safety note supervise children with sharp tools and use products according to their labels.
4. Introduce woodworking to develop problem-solving and creativity.

Woodworking teaches measuring, cutting, joining and finishing to make useful items from wood. Basic hand tools and simple power tools combined with knowledge of grain, fasteners and common joints provide practical skills through hands-on projects.
This skill builds problem-solving, spatial reasoning and creativity while producing useful repairs and items. Start with a small project like a shelf, sketch a plan and measure twice before cutting. Rule of thumb use the right tool and keep blades sharp. Safety note wear eye protection, clamp work securely and follow safe operating practices for any power tools.
5. Demonstrate map reading and navigation without digital devices.

Map reading and traditional navigation cover interpreting maps, using a compass and estimating distance by scale and pacing. Skills like orienting a map, taking bearings and matching symbols to terrain help people find their location and plan routes without electronic aids.
Traditional navigation matters for outdoor safety and spatial awareness. Practice on familiar paths, orient the map to north, confirm position with two landmarks and estimate distance by pacing. Rule of thumb keep a paper map and a compass as backups and tell someone your route. Safety note carry water, a light source and basic first aid when traveling beyond familiar areas.
6. Teach basic first aid to help handle common minor injuries.
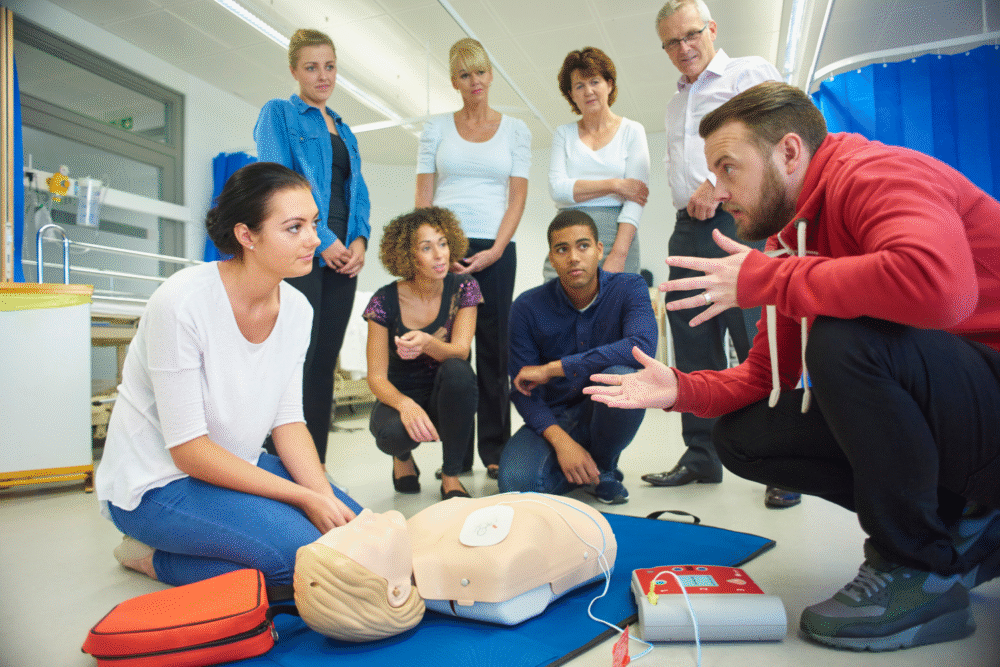
Basic first aid covers assessing a scene, prioritizing safety, stopping minor bleeding, cleaning and dressing wounds, and recognizing when to seek emergency care. Training emphasizes calm response, simple hands-on steps and when to summon professional help.
These skills can reduce harm and increase confidence in everyday emergencies. Practical tip is to pack a basic kit with bandages, antiseptic wipes and tape, and practice with a certified course. Rule of thumb get professional help for severe bleeding, unconsciousness or breathing problems. Safety note consult a qualified professional for personalized medical advice and hands-on training.
7. Show how to preserve food through canning and drying methods.

Canning and drying preserve food by sealing or removing moisture to prevent spoilage. Canning uses jars and proper heat or pressure, while drying reduces water content; both rely on clean equipment and correct method to be safe and effective.
Food preservation reduces waste and builds pantry independence, but safety matters. Practical idea could be to start with simple dried fruits or herbs and use tested recipes for canning, label and date jars and rotate supplies. Rule of thumb discard jars with bulging lids or odd odors. Safety note follow approved canning guidelines and seek hands-on instruction from extension services or qualified instructors before trying home canning.
8. Encourage learning calligraphy to improve handwriting and focus.

Calligraphy is forming letters with intentional strokes using tools like brush pens or nibs and ink. Learning basic strokes, spacing and rhythm develops control of pressure and angle and builds consistent forms that improve handwriting and lettering skills.
Calligraphy enhances focus, fine motor control and visual communication. Practice basic drills, use beginner pens and aim for short daily practice to build muscle memory. Rule of thumb prioritize consistent spacing and letter shapes rather than speed. Applications include invitations, journaling and signage. Safety note rest hands regularly and use good posture to avoid strain.
9. Instruct on candle making for practical and emergency use.
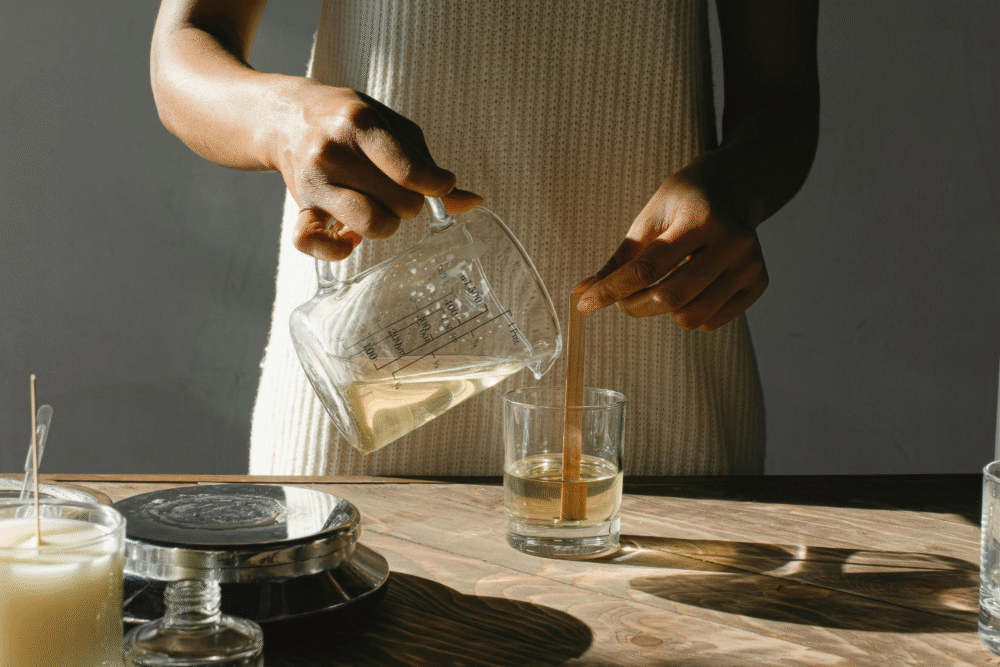

Candle making melts wax, matches it with a properly sized wick and pours into vessels to create a controlled flame. Basic understanding of wax types and temperature control helps produce candles that burn evenly.
This craft supplies practical light for emergencies and makes thoughtful handmade items. Begin with a small container candle using a tested method, trim wicks before burning and keep candles on heat-resistant surfaces. Rule of thumb never leave a flame unattended. Safety note handle hot wax with care, keep flammables away and practice safe extinguishing.
10. Share storytelling techniques to enhance communication and memory.

Storytelling techniques teach how to shape information with a clear beginning, middle and end, and use sensory detail, pacing and repetition to make messages memorable. Practicing concise language and meaningful scenes helps listeners follow logic and retain key points.
Strong storytelling improves communication, persuasion and memory in everyday situations. Practice short personal anecdotes, focus on one clear takeaway, and use sensory anchors to aid recall. Use repetition and visual cues to strengthen memory of key points. Rule of thumb keep stories concise and relevant and ask for feedback to improve. Consider targeted coaching for high-stakes presentations.
