Discover how growing up financially challenged builds resilience and shapes lasting wealth values for life.

Growing up in a financially challenged environment often means facing scarcity and limited resources from a young age. This experience teaches important life skills such as resourcefulness, frugality, and emotional strength, helping individuals develop a practical understanding of money beyond just spending.
Understanding these lessons is crucial because they build resilience and promote a long-term mindset about wealth. By embracing the values of delayed gratification and adaptability, readers can learn to manage finances wisely and prioritize stability over short-term indulgence.
1. Growing up with limited resources teaches creative problem-solving skills.
Growing up with limited resources teaches creative problem-solving skills by forcing people to find workarounds, repurpose items, and improvise solutions when standard options are out of reach. Children raised in scarcity often learn to break problems into manageable pieces, weigh trade-offs, and experiment with low-cost alternatives, developing a knack for practical innovation rather than relying on purchasing power.
For everyday readers, that habit translates into faster, cheaper solutions to household and financial challenges. Try keeping a simple repair before replace checklist and a monthly challenge to repurpose one item instead of buying new. A useful rule of thumb is to ask if something can be fixed within a weekend before replacing it.
2. Experiencing scarcity fosters a deeper appreciation for financial stability.
Experiencing scarcity fosters a deeper appreciation for financial stability by making the cost of unexpected expenses and regular bills tangible. When families have limited cushions, prioritizing essentials, anticipating shortfalls, and valuing predictable income become everyday lessons that shape cautious and forward-looking money behaviors.
Many people carry that appreciation into adulthood as a preference for emergency savings and stable choices. Start by building a small emergency reserve equal to a few weeks of living costs and automate contributions if possible. One practical step is to treat savings like a recurring bill to preserve stability and reduce stress in tight months.
3. Facing financial challenges early builds strong emotional resilience.

Facing financial challenges early builds strong emotional resilience because repeated setbacks teach coping strategies and perspective. Children who navigate budget constraints often develop patience, the ability to tolerate uncertainty, and a comfort with delayed outcomes, which together form an emotional toolkit for handling adversity in work and relationships.
Readers can translate that hard-earned endurance into calmer decision making and better stress management. Try a simple resilience practice: name one past financial challenge you overcame and list two skills you used, then apply one skill this week. For issues that feel overwhelming seek professional support from a qualified counselor for personal advice.
4. Learning to budget from a young age encourages smart money management.
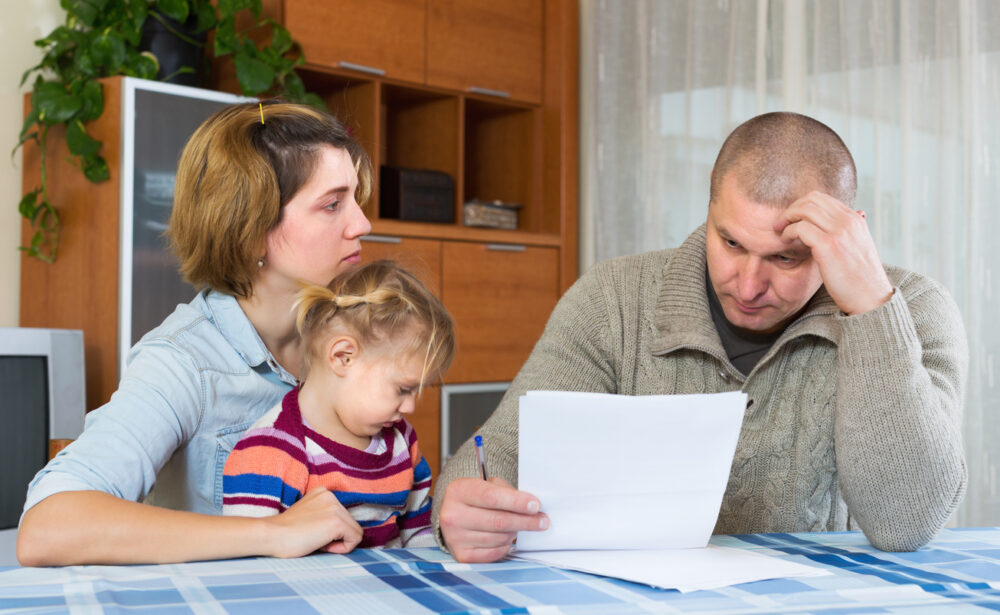

Learning to budget from a young age encourages smart money management by making priorities visible and trade-offs explicit. When families model tracking income and expenses, children pick up skills like categorizing spending, setting short-term goals, and adjusting choices to fit limited funds, which become lifelong financial habits.
Practical application is straightforward and empowering for day to day life. A concrete tip is to follow a 50 30 20 style checklist adapted to your situation and review it monthly to stay on track. For major financial decisions consult a qualified financial professional for personal advice when needed.
5. Financial constraints nurture gratitude for even small material comforts.

Financial constraints nurture gratitude for even small material comforts by sharpening attention to what truly adds value to daily life. When resources are scarce, people learn to savor modest pleasures and recognize the difference between fleeting wants and lasting needs, building an appreciative perspective that resists consumer pressure.
That perspective can reduce impulse purchases and increase satisfaction with less. A helpful exercise is to list three small things you used today that brought value and keep that list for a week to encourage mindful spending. As a general rule, wait 48 hours before buying nonessential items to test if they still matter.
6. Overcoming hardship develops persistence and determination to succeed.

Overcoming hardship develops persistence and determination to succeed because repeated effort in the face of limited means teaches goal orientation and grit. Young people who must navigate obstacles to access education, work, or basic needs often learn to set long-term aims, break them into achievable steps, and keep returning after setbacks.
Those traits boost career and personal progress by turning setbacks into learning opportunities. To harness this, create a simple persistence plan with one long-term goal, three short milestones, and regular progress check ins. If emotional barriers arise consider talking with a trusted mentor or counselor for personalized support.
7. Witnessing sacrifices cultivates empathy and thoughtful spending habits.

Witnessing sacrifices cultivates empathy and thoughtful spending habits by showing the human side of money choices. When family members forego comforts or prioritize another person’s needs, children learn to weigh the social impacts of purchases and to consider how resources affect wellbeing beyond individual wants.
That lesson often leads to more intentional consumption and generosity as adults. Try a practical rule of thumb: before making a sizable purchase ask who benefits and whether a smaller option would meet the same need. Volunteering locally can also reinforce compassionate budgeting and perspective.
8. Adapting to financial limitations enhances flexibility in life decisions.

Adapting to financial limitations enhances flexibility in life decisions by teaching people to evaluate multiple pathways and accept trade offs. Limited resources encourage prioritizing what matters most, postponing nonessential plans, and finding alternative routes to goals, which makes long term planning more resilient to change.
You can apply this adaptability to everyday choices by creating backup plans and ranking options by importance. An actionable step is to list three possible ways to reach a goal with different cost levels and choose the one that balances time and expense. For significant life changes consider consulting trusted advisors to weigh trade offs.
9. Building wealth values through firsthand understanding of money’s true worth.

Building wealth values through firsthand understanding of money’s true worth means recognizing that money is a tool for security, freedom, and choices rather than only a means of consumption. Growing up with tight budgets often teaches the real costs of debt, the benefits of saving, and how steady habits compound into options in the future.
That insight encourages long term financial thinking and prudent priorities. One concrete step is to track one recurring expense for a month and redirect a portion of it into a simple savings account. When complex financial decisions arise seek guidance from a qualified professional for personalized advice.
10. A modest upbringing encourages prioritizing experiences over material possessions.

A modest upbringing encourages prioritizing experiences over material possessions by showing how relationships, learning, and memories offer durable satisfaction at low cost. Limited funds often push families to invest time and creativity in gatherings, hobbies, and shared activities that create meaning without high spending.
Applying this mindset can improve wellbeing and reduce wasteful consumption. A quick tip is to plan one low cost experience each month with friends or family and treat it as a budgeted priority. Keep in mind that balance is important and occasional treats can be part of a healthy approach to enjoying life.
